
Dɛn ne Aboɔden abo a Wɔayɛ, Nneɛma a Wɔasuasua ne Nneɛma a Wɔde Yɛ Nneɛma a Wɔde Yɛ Nneɛma?
 Wɔ aboɔden abo wiase no mu no, aboɔden abo bi wɔ hɔ a wɔabɔ sɛ wɔmfa suasua abɔde anaasɛ wɔde bɛbɔ mmɔden na wɔayɛ sɛ abɔde. Wɔfrɛ saa aboɔden abo yi sɛ nneɛma a wɔde yɛ nneɛma, nea wɔde asuasua, anaa nea wɔde yɛ ne ho. Yɛrekɔhwehwɛ nea nsonsonoe no yɛ ne nea aboɔden abo a wɔtaa hu wɔ gua so no yɛ.
Wɔ aboɔden abo wiase no mu no, aboɔden abo bi wɔ hɔ a wɔabɔ sɛ wɔmfa suasua abɔde anaasɛ wɔde bɛbɔ mmɔden na wɔayɛ sɛ abɔde. Wɔfrɛ saa aboɔden abo yi sɛ nneɛma a wɔde yɛ nneɛma, nea wɔde asuasua, anaa nea wɔde yɛ ne ho. Yɛrekɔhwehwɛ nea nsonsonoe no yɛ ne nea aboɔden abo a wɔtaa hu wɔ gua so no yɛ.
Nea edi kan, Nkyerɛase ahorow bi
Synthetic – Synthetic aboɔden aboɔ yɛ aboɔden aboɔ a onipa na ɔyɛ nanso ɛwɔ abɔdeɛ mu yɔnko. Wɔwɔ honam fam, nnuru, ne aniwa su te sɛ abɔde mu ɔbo no.
Imitation anaa Simulant – Eyinom yɛ aboɔden abo a ɛbɔ mmɔden sɛ ɛbɛyɛ te sɛ aboɔden abo ankasa, abɔde mu aboɔden abo nanso wɔde ade soronko koraa na ɛyɛe. Ebia ɛbɛyɛ aboɔden abo foforo (a mpɛn pii no ne bo yɛ mmerɛw) anaasɛ ade a ɛnyɛ aboɔden abo te sɛ plastic anaa resin.
Abɔde mu Aboɔden abo
Abɔde mu aboɔden abo yɛ aboɔden abo biara a wɔatu afiri fam na wɔatwitwa ayɛ no aboɔden abo. Wobetumi de akwan horow ayɛ wɔn ho adwuma na ama kɔla ne nea emu da hɔ atu mpɔn, te sɛ ɔhyew, nanso ɛsɛ sɛ aboɔden abo titiriw no fi abɔde mu. Abɔde mu aboɔden abo tumi gye mfe ɔpepem pii na wɔabɔ na nkurɔfo ani agye wɔn ahoɔfɛ ho fi bere mfiase.

Aboɔden abo a Wɔayɛ
Aboɔden abo a wɔayɛ ne nea ɛsuasua abɔde mu abo pɛpɛɛpɛ nanso onipa na ɔyɛe wɔ aduruyɛdan mu. Aboɔden abo a wɔtaa yɛ ne abohene a wɔayɛ , safir a wɔayɛ , ne quartz a wɔayɛ . Aboɔden abo a wɔayɛ no wɔ nnuru a wɔde yɛ nneɛma, sɛnea ɛte sɛ ahwehwɛ, ne ne su te sɛ abɔde mu aboɔden abo no pɛpɛɛpɛ. Ɛyɛ den yiye ma onimdefo a ɔntete no sɛ obehu nsonsonoe a ɛda aboɔden abo a wɔde ayɛ ne abɔde mu aboɔden abo ntam.

Aboɔden abo a Wɔde Suasua Anaasɛ Wɔde Yɛ Simulant
Nneɛma a wosuasua anaasɛ nea wɔde yɛ mfonini yɛ aboɔden abo a ɛbɔ mmɔden sɛ ɛbɛyɛ te sɛ ade ankasa. Aboɔden abo a wɔtaa yɛ a wɔde yɛ mfonini anaasɛ wɔde suasua a wohu wɔ gua so ne nea wɔbɔ mmɔden sɛ wɔbɛyɛ daimond bi. Wɔde nnuru a wɔde yɛ nneɛma te sɛ rutile a wɔayɛ anaa strontium titanate adi dwuma mfe du du pii de abɔ mmɔden na wɔayɛ sɛnea daimond hyerɛn no ayɛ.
Ɛwom mpo sɛ onipa na ɔyɛɛ aboɔden abo yi de, nanso enni honam fam su ne nnuru a ɛwɔ mu te sɛ abɔde mu aboɔden abo a wosuasua no. Eyi nti na wɔmfa wɔn nhyɛ mu sɛ nneɛma a wɔde yɛ nneɛma.
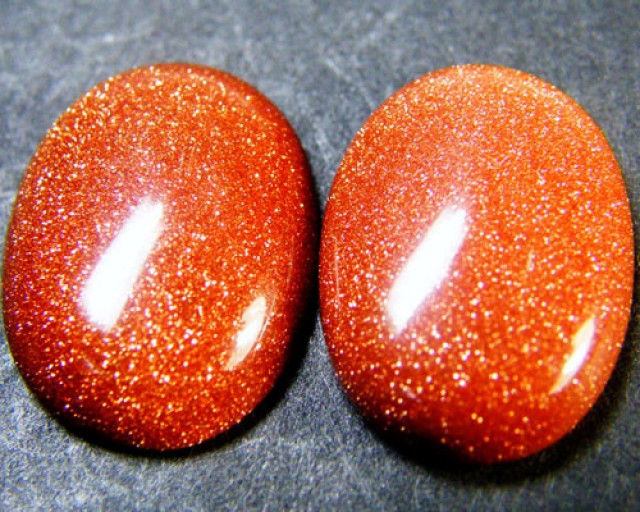
Ahwehwɛ ne plastic yɛ nneɛma afoforo a wɔtaa suasua a wobetumi ahu. Wɔtaa de ahwehwɛ bruu ma sɛ safir bruu ma adetɔfo a wonsusuw ho, bere a wobetumi atɔn plastic nhwiren sɛ abɔde mu nhene. Goldstone yɛ ahwehwɛ a onipa ayɛ a ɛwɔ nsensanee a ɛyɛ sika kɔkɔɔ wɔ ne nyinaa mu a wɔtaa tɔn sɛ abɔde mu owia abo (mfonini a ɛwɔ ase hɔ no).

Dɛn Ne Aboɔden abo a Wɔtaa Yɛ a Wɔde Yɛ Nneɛma?
Wɔayɛ aboɔden abo a wɔde ayɛ nneɛma fi 1800 mfe no mfiase enti ɛnyɛ ade foforo. Gyidi a ɛnteɛ wɔ hɔ sɛ tete vintage style Jewelry ntumi nyɛ synthetic efisɛ nkurɔfo gye di sɛ mfiridwuma a wɔde yɛ synthetic aboɔden abo no nni hɔ saa bere no. Nokwasɛm ne sɛ wɔde aboɔden abo a wɔde ayɛ nneɛma ahyɛ vintage Jewelry mu ma efisɛ ɛde besi nnansa yi no na mfiridwuma nni hɔ a wɔde behu nneɛma a wɔayɛ no.
Mfiase no wɔyɛɛ nneɛma a wɔde yɛ nneɛma dodow no ara de yɛɛ mfiridwuma. Quartz pɔtee na wɔde di dwuma wɔ ɛlɛtrɔnik nneɛma pii mu. Sɛ wobenya quartz a ɛho tew a wɔmfa biribiara nka ho pii a, ne bo yɛ den na egye bere pii, enti wɔyɛɛ ɔkwan bi a wɔfa so nyin quartz wɔ afiri a wɔde yɛ nhwehwɛmu mu. Saa kwan no so no, na wobetumi adi ade a etwa to no so. Safire a wɔayɛ a wɔde di dwuma wɔ watch anim ne smart phone mu yɛ ɔkwan foforo a wɔfa so yɛ aboɔden abo a wɔayɛ de di dwuma da biara da.

Bere a wɔde saa mfiridwuma yi bae no, tumi a wɔde yɛ nneɛma a ɛyɛ aboɔden abo a wobetumi ayɛ no afã horow no ba. Aboɔden abo a wɔde ayɛ a wɔtaa yɛ ne
Safir anaa Ruby (Abɔde a wɔfrɛ no Corundum) .
Diamond a wɔde yɛ nneɛma
Emerald a wɔfrɛ no Emerald
Spinel a ɛyɛ den
Quartz, Amethyst , Citrine , ne Ametrine a wɔde yɛ nneɛma
Opal na ɔkyerɛwee
Chrysoberyl ne Alexandrite a wɔde yɛ nneɛma
Ɔkwan Bɛn so na Wɔbɔ Aboɔden abo a Wɔayɛ no?
Akwan kakraa bi na wobetumi afa so ayɛ aboɔden abo a wɔayɛ. Ɔkwan a edi kan a wonim no sɛ ogyaframa fusion kwan no ne ɔkwan a ɛyɛ mmerɛw na ne bo nyɛ den sen biara a wɔfa so yɛ aboɔden abo a wɔayɛ. Ɔkwan biara gyaw ‘nsateaa nkyerɛwee’ a ɛyɛ ketewaa bi wɔ aboɔden abo no mu a wobetumi de adi dwuma de ahu.
Ogya Fusion anaa Verneuil Adeyɛ
Wɔde powder a nneɛma a ɛfata a wɔde yɛ aboɔden abo wom fa ogyaframa a ɛyɛ hyew mu baabi a ɛwosow kɔ asɛnka agua a twitwiw so. Sɛ nsu no dwo a, ɛyɛ ahwehwɛ ma ɛbɛyɛ aboɔden abo a wɔayɛ. Nhwɛsoɔ bɛyɛ Aluminium Oxide a sɛ ɛyɛ hyew na ɛyɛ nwini a ɛbɛdan corundum (sapphire anaa ruby ). Wɔtaa de saa kwan yi na ɛyɛ spinel , safir, ne ruby.

Czochralski Adeyɛ anaa Ɔkwan a Wɔfa so Twe
Nea ɛka saa kwan yi ho ne sɛ wɔbɛbɔ aduru a aduannuru pii wom wɔ ahina mu. Wɔde aba bi na efi ase nyin. Mpɛn pii no, aba yɛ aboɔden abo a wɔpɛ no kakraa bi, sɛ nhwɛso no, alexandrite . Wɔde aba no hyɛ aduru no mu baabi a efi ase yɛ ahwehwɛ no. Wɔde nkakrankakra twe aba no fi aduru no mu na bere a ɛredwo no, ahwehwɛ no kɔ so yɛ. Aboɔden abo a wɔtaa de saa kwan yi yɛ ne chrysoberyl ne alexandrite, corundum ne garnet .

Flux Ɔkwan a Wɔfa so Yɛ
Flux kwan no yɛ akwan a ne bo yɛ den sen biara a wɔfa so yɛ aboɔden abo a wɔde ayɛ nneɛma no mu biako. Adeyɛ no hwehwɛ sɛ wɔde Flux ade a ɛyɛ den bi bɛpete aduannuru afoforo mu. Sɛ saa aduru yi fi ase dwo a, ahwehwɛ no ba mu. Wɔtaa de eyi di dwuma ma emerald , nanso wobetumi de akɔ asɛnnibea nso wɔ spinel, sapphire, ruby ne alexandrite ho.

Ɔkwan a Wɔfa so Yɛ Nsu mu Ɔhyew
Eyi nkutoo ne ɔkwan a wonim a ebetumi ayɛ quartz a wɔayɛ. Sɛ wunim sɛnea quartz yɛ wɔ abɔde mu a, wubehu sɛ wɔde edin koro no ara ‘hydrothermal’ na edi dwuma.
Hydrothermal kyerɛ sɛ wɔbɔɔ no wɔ nsu mu. Wɔ abɔde mu no, sɛ tokuru bi wɔ asase mu a nsu a ɛyɛ hyew kɛse a aduannuru pii wom ahyɛ mu ma a efi ase dwo a, quartz benyin. Eyi ne ɔkwan a wɔfa so bɔ amethyst geodes .
Nsu mu hyew kwan no suasua saa abɔde mu adeyɛ yi denam tebea a ɛyɛ hyew kɛse a ɛma nsu a aduannuru wom no yɛ nwini nkakrankakra no so. Nnuannuru a ɛwɔ nsu no mu no fi ase yɛ ahwehwɛ na ɛma ɛyɛ quartz a wɔayɛ.
Ti nhwi a Wɔyɛ no Nwene Adeyɛ
Wɔde saa kwan yi yɛ cubic zirconia . Ɛte sɛ Flux Method nanso nsuo no hia sɛ ɛyɛ super hot. Sɛnea ɛbɛyɛ a nsu no bɛkɔ so no, wɔma anwenne no akyi dwo sɛnea ɛbɛyɛ a nsu no bɛdwo na ayɛ “Skull cap” a nsu a ɛyɛ hyew kɛse no wom. Bere a nsu no dwo no ɛma ɛyɛ cubic zirconia ahwehwɛ a ɛyɛ pɛ.
CVD (Nnuru a Wɔde Yɛ Nsuonwini) .
Eyi yɛ akwan abien a wonim sɛ wɔfa so yɛ Diamond a wɔayɛ no foforo no mu biako. CVD Wɔbɔ Diamond wɔ vacuum mu a carbon atom ahorow no de nkakrankakra tɔ gu nnyinaso bi so.

HPHT (High Pressure Ɔhyew a Ɛkorɔn) .
Wɔde dade nkuku akɛse a wɔfrɛ no ‘presses’ na ɛyɛ HPHT diamonds de yɛ nhyɛso ne ɔhyew a ɛtra so a ɛwɔ asase ase tɔnn no ho mfonini. Wotumi ma wim tebea a ɛboro 60,000 nya nhyɛso ne ɔhyew a ɛkɔ soro kodu digrii Celsius 1500. HPHT Diamond a ɛso sen biara sɛnea ɛte nnɛ no yɛ ɔbo a ne kɛse yɛ 10.02ct ahinanan a ne kɔla yɛ ‘E’ na emu da hɔ VS1.

Dɛn Ne Aboɔden abo a Wɔtaa Suasua Anaasɛ Wɔde Yɛ Adwuma?
Sɛnea yɛadi kan aka no, aboɔden abo a wɔde suasua anaasɛ wɔde yɛ no yɛ biribi a ɛbɔ mmɔden sɛ ebesuasua abɔde mu aboɔden abo nanso ɛyɛ biribi soronko koraa. Ase hɔ no yɛ nneɛma a wɔtaa suasua no din.
Spinel a Wɔde Nneɛma Ayɛ
Ɛnyɛ den sɛ wɔde Flame Fusion kwan no bɛyɛ spinel a wɔayɛ no na ɛwɔ kɔla ahorow ahorow. Wubehu sɛ wɔretɔn spinel a wɔayɛ no sɛ safir, aquamarine , anaa peridot . Ɛyɛ ade a ɛyɛ den yiye, enti ntease wom sɛ wode spinel a wɔayɛ no bɛyɛ nneɛma a wosuasua.
Rutile a Wɔayɛ, Strontium Titanate, Moissanite a Wɔayɛ, YAG, ne GGG
Nnipa na wɔyɛɛ saa aboɔden abo anum yi nyinaa, ɛwom sɛ rutile ne moissanite biara wɔ abɔde mu yɔnko de. Wɔaboaboa wɔn nyinaa ano efisɛ nea wɔde di dwuma titiriw ne sɛ wɔbɛyɛ daimond simulant. Rutile a wɔayɛ ne strontium titanate (ɛnyɛ sɛ wɔde fra titanite) nyinaa wɔ apete a ɛyɛ nwonwa (ogya a wuhu wɔ abohene mu) enti wɔtaa de si abohene ananmu. YAG ne GGG nyinaa yɛ garnets (yttrium aluminum garnet ne gadolinium gallium garnet) a ɛte sɛ Diamonds hwɛbea.

Synthetic moissanite yɛ diamond simulant foforo koraa na ne hwɛbea no bɛn abɔde mu diamond sen biara. Nea ɛyɛ aboɔden abo yi fɛ ne sɛ wobetumi ayɛ no bɛyɛ sɛ nea enni kɔla mmom sen sɛ ɛbɛyɛ bruu anaa kɔkɔɔ a nneɛma afoforo a wɔde yɛ daimond ho mfonini hu amane wɔ ho. Nna yi, wɔtɔn moissanite a wɔayɛ no sɛ aboɔden abo wɔ n’ankasa mu a wɔntɔn sɛ nea wɔde yɛ no sɛnea ɛte.
Kubik Zirconia a ɛwɔ hɔ
Eyi ne aboɔden abo a wɔtaa de di dwuma na wɔde di dwuma kɛse a wɔde suasua. Wobetumi de kɔla ahorow ahorow ayɛ na ɛyɛ aboɔden abo bi a wɔde besi ananmu a ɛyɛ nokware. Cubic zirconia ne zircon nni abusuabɔ biara . Bere a edin no di nsɛ no, wɔyɛ aboɔden abo a ɛsono emu biara koraa. Te sɛ apɔw-mu-teɛteɛ ne akutu kakra.
Abobɔdeɛ
Ɛkame ayɛ sɛ wɔtaa de suasua aboɔden abo biara a ɛyɛ simulant a akyɛ sen biara a wonim. Ahwehwɛ a ɛyɛ kɔla biara a wobɛbɔ no yɛ mmerɛw enti sɛ wobɛma ahwehwɛ aboɔden abo ayɛ te sɛ ade ankasa no yɛ mmerɛw wɔ saa simulant yi mu.
Plastik a wɔde yɛ nneɛma
Te sɛ ahwehwɛ no, wobetumi de plastic asuasua aboɔden abo pii a ɛnyɛ hann. Wobetumi ama ayɛ te sɛ malachite anaa turquoise na ɛtɔ mmere bi a wɔde suasua opal (wɔtaa frɛ no opalite).
Wɔ Gem Rock Auctions so no, wɔabara sɛ wɔbɛtɔn aboɔden abo a wɔayɛ anaa wɔayɛ no sɛnea ɛte. Wubetumi de ahotoso atɔ nneɛma a ɛyɛ aboɔden abo a efi abɔde mu nyinaa.
SHOP FOR ABƆDEƐ MU AGYINATUO
搜尋Gemstone Encyclopedia
相關拍賣
相關文章
Obiara wɔ aboɔden abo a ɛne ne nsoromma agyiraehyɛde hyia. Wɔsan frɛ eyinom sɛ wo Nsoromma Abo. Sua pii fa saa abo yi ho na hwehwɛ nea wo Nsoromma Abo no yɛ.
10th May 2018
Mfiase no na wɔde Awo Abo anaa aboɔden abo no bata nsoromma mu hwɛ anaa ɔsram a ankorankoro bi awo ho. Hwehwɛ nea wo bo no yɛ na hwɛ abo a yɛwɔ sɛ yɛtɔn no
8th Feb 2021
Nnwinnade pii wɔ gua so a wɔde sɔ ɔbo a ɛsom bo hwɛ, nanso dɛn ne nnwinnade atitiriw a wɔhwehwɛ ma nhwehwɛmu a ɛnyɛ den. Momma yɛnhwɛ nnwinnade anan a wɔde sɔ aboɔden abo hwɛ.
4th Mar 2020
最新的文章
Forsterite yɛ peridot a ɛyɛ aboɔden abo a ɛyɛ aboɔden abo a ne bo yɛ fã bi, a ɛyɛ lime kosi ngodua ahabammono a efi olivine aboɔden abo ahorow kuw no mu no mu aboɔden abo.
26th Feb 2026
Okenite yɛ aboɔden abo a ɛntaa nsi, a ɛte sɛ kotoku a wonim no sɛ ɛyɛ fɛ te sɛ mununkum. Hwehwɛ ne ntease, ne bo, ɔhwɛ ho afotu, abakɔsɛm, mfiase, ne mineral ho nsɛm a ɛkɔ akyiri wɔ akwankyerɛ a edi mũ yi mu.
17th Feb 2026
Heulandite ahwehwɛ fi zeolite mineral abusua no mu na ɛwɔ “funka nsɛso.” Wɔtaa yɛ pink, fitaa, ahabammono, anaa borɔdɔma, na wɔyɛ ahwehwɛ a ahoɔden wom a ɛsa yare. Gem Rock Auctions kyɛ biribiara a ɛsɛ sɛ wuhu fa heulandite ahwehwɛ ho.
12th Feb 2026
文章類別
How To's is where you will find helpful articles from gem Rock Auctions on how to cut gemstones, select gemstones and buy gemstones.
9文章








