
¿Qué son las piedras preciosas sintéticas, imitaciones y simulantes?
 En el mundo de las piedras preciosas , existen gemas creadas para imitar la naturaleza o para intentar asemejarse a ella. Estas gemas se denominan sintéticas, imitaciones o simulantes. Exploraremos la diferencia y cuáles son las gemas más comunes en el mercado.
En el mundo de las piedras preciosas , existen gemas creadas para imitar la naturaleza o para intentar asemejarse a ella. Estas gemas se denominan sintéticas, imitaciones o simulantes. Exploraremos la diferencia y cuáles son las gemas más comunes en el mercado.
Primero, algunas definiciones
Sintéticas : Las gemas sintéticas son gemas creadas por el hombre, pero con una contraparte natural. Poseen las mismas propiedades físicas, químicas y ópticas que la piedra natural.
Imitación o Simulador : Son piedras preciosas que intentan parecerse a piedras preciosas naturales reales, pero están hechas de un material completamente diferente. Pueden ser de otra piedra preciosa (a menudo más económica) o de un material no gemológico, como plástico o resina.
Piedras preciosas naturales
Las piedras preciosas naturales son cualquier mineral extraído de la tierra y tallado hasta obtener una gema. Pueden tratarse con diferentes técnicas para mejorar su color y claridad, como el calor, pero el mineral principal debe provenir de la naturaleza. Su creación puede tardar millones de años y la humanidad ha quedado fascinada por su belleza desde tiempos inmemoriales.

Piedras preciosas sintéticas
Las gemas sintéticas son aquellas que imitan con exactitud las piedras naturales, pero son creadas por el hombre en un laboratorio. Las gemas sintéticas más comunes son los diamantes sintéticos, los zafiros sintéticos y el cuarzo sintético. Las gemas sintéticas tienen exactamente la misma composición química, estructura cristalina y propiedades que las gemas naturales. Es muy difícil para un experto sin formación distinguir entre una gema sintética y una natural.

Piedras preciosas de imitación o simulantes
Las imitaciones o simulantes son piedras preciosas que intentan imitar el diamante real. Las imitaciones o simulantes más comunes en el mercado son aquellas que intentan replicar el diamante. Simuladores como el rutilo sintético o el titanato de estroncio se han utilizado durante décadas para intentar replicar el brillo del diamante.
Aunque estas piedras preciosas son creadas por el hombre, no tienen las mismas propiedades físicas ni composición química que la gema natural que imitan. Por eso no se clasifican como sintéticas.
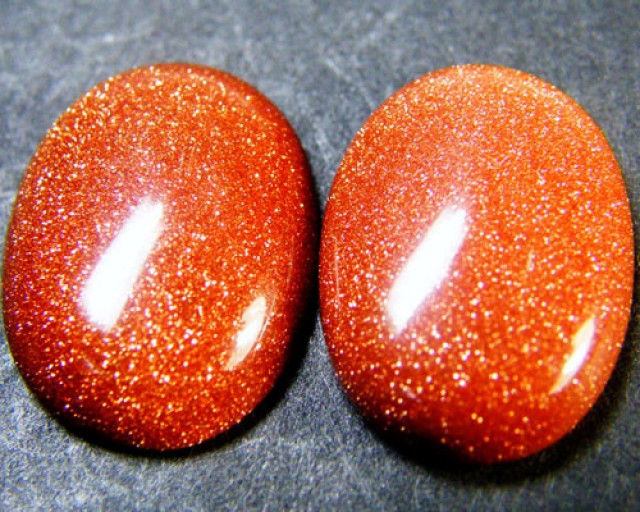
El vidrio y el plástico son otras imitaciones comunes. El vidrio azul suele ofrecerse como zafiro azul a compradores desprevenidos, mientras que las cuentas de plástico pueden venderse como perlas naturales. La piedra dorada es un vidrio artificial con vetas doradas que suele venderse como piedra solar natural (imagen inferior).

¿Cuáles son las piedras preciosas sintéticas más comunes?
Las piedras preciosas sintéticas se han producido desde principios del siglo XIX, por lo que no son algo nuevo. Existe la creencia errónea de que la joyería antigua de estilo vintage no puede ser sintética, ya que se cree que la tecnología utilizada para crear piedras preciosas sintéticas no existía en aquel entonces. Lo cierto es que la joyería vintage está plagada de piedras preciosas sintéticas porque, hasta hace poco, no existía la tecnología para detectarlas.
La mayoría de los materiales sintéticos se crearon originalmente con fines industriales. El cuarzo, en particular, se utiliza en numerosos componentes electrónicos. Encontrar grandes cantidades de cuarzo puro y sin inclusiones es costoso y requiere mucho tiempo, por lo que se desarrolló un proceso para cultivar cuarzo en laboratorio. De esta forma, se podía controlar el producto final. El zafiro sintético para su uso en esferas de relojes y teléfonos inteligentes es otra forma de crear minerales sintéticos para el uso diario.

Con la introducción de esta tecnología, surge la posibilidad de crear material de calidad gema que se puede facetar. Las piedras preciosas sintéticas más comunes son
Zafiro o Rubí (El mineral Corindón)
Diamante
Esmeralda
Espinela
Ópalo
Crisoberilo y alejandrita
¿Cómo se crean las piedras preciosas sintéticas?
Existen diversas maneras de crear gemas sintéticas. El método más antiguo, conocido como fusión por llama, es el más sencillo y económico. Cada método deja una huella microscópica en el interior de la gema, que puede utilizarse para su detección.
Fusión por llama o proceso Verneuil
El polvo que contiene los elementos necesarios para la fabricación de un mineral se pasa a través de una llama caliente, donde se funde sobre una plataforma giratoria. Al enfriarse, el líquido cristaliza en una gema sintética. Un ejemplo sería el óxido de aluminio, que al calentarse y enfriarse se transforma en corindón (zafiro o rubí). La espinela , el zafiro y el rubí se crean comúnmente mediante este método.

Proceso Czochralski o método de tracción
Este método consiste en fundir una solución rica en nutrientes en un crisol. Se utiliza una semilla para iniciar el proceso de crecimiento. Una semilla suele ser una pequeña cantidad del mineral deseado, por ejemplo, alejandrita . La semilla se sumerge en la solución donde comienza la cristalización. Se extrae lentamente de la solución y, a medida que se enfría, continúa la cristalización. Las piedras preciosas comunes que se obtienen con este método son el crisoberilo , la alejandrita, el corindón y el granate .

Método de flujo
El método de fundente es uno de los más costosos para crear una gema sintética. El proceso consiste en disolver un fundente sólido con otros nutrientes. Cuando esta solución comienza a enfriarse, se forman los cristales en su interior. Este método se utiliza comúnmente para las esmeraldas , pero también se puede utilizar para la espinela, el zafiro, el rubí y la alejandrita.

Método hidrotermal
Este es el único método conocido para crear cuarzo sintético. Si conoces cómo se forma el cuarzo en la naturaleza, notarás que se utiliza el mismo nombre: «hidrotermal».
Hidrotermal significa que se crea en el agua. En la naturaleza, cuando una cavidad en la tierra está llena de agua muy caliente y rica en nutrientes y comienza a enfriarse, crece cuarzo. Así es como se forman las geodas de amatista .
El proceso hidrotermal imita este fenómeno natural creando un ambiente extremadamente cálido donde el agua rica en nutrientes se enfría lentamente. Los nutrientes del agua comienzan a cristalizarse y a crear cuarzo sintético.
Proceso de fusión del cráneo
Este proceso se utiliza para la creación de zirconia cúbica . Es similar al método de fundente, pero el líquido debe estar muy caliente. Para contenerlo, se enfría el exterior del recipiente, creando una especie de "casquete" que lo contiene. Al enfriarse, el líquido crea cristales perfectos de zirconia cúbica.
CVD (deposición química de vapor)
Esta es una de las dos formas conocidas de crear diamantes sintéticos. Los diamantes CVD se crean al vacío, donde los átomos de carbono se precipitan lentamente sobre una base.

HPHT (alta presión y alta temperatura)
Los diamantes HPHT se crean utilizando enormes recipientes de acero llamados "prensas" para simular la presión y temperatura extremas de las profundidades terrestres. Son capaces de producir más de 60.000 atmósferas de presión y temperaturas de hasta 1500 grados Celsius. El diamante HPHT más grande hasta la fecha es una piedra cuadrada de 10,02 ct, de color "E" y claridad VS1.

¿Cuáles son las piedras preciosas de imitación o simulantes más comunes?
Como mencionamos anteriormente, una imitación o simulación de una gema es aquella que intenta imitar una gema natural, pero está compuesta de un material completamente diferente. A continuación, se presenta una lista de las imitaciones más comunes.
Espinela sintética
La espinela sintética se fabrica fácilmente mediante el método de fusión a la llama y está disponible en una variedad de colores. La encontrará en forma de zafiro, aguamarina o peridoto . Es un material muy duro, por lo que es lógico fabricar imitaciones de espinela sintética.
Rutilo sintético, titanato de estroncio, moissanita sintética, YAG y GGG
Estos cinco minerales son sintéticos, aunque el rutilo y la moissanita tienen una contraparte natural. Se han agrupado porque su principal uso es simular diamantes. El rutilo sintético y el titanato de estroncio (que no debe confundirse con la titanita) presentan una dispersión increíble (el fuego que se observa en los diamantes), por lo que se utilizan comúnmente para reemplazarlos. El YAG y el GGG son granates (el granate de itrio y aluminio y el granate de gadolinio y galio) que se asemejan a los diamantes.

La moissanita sintética es el simulante de diamante más reciente y su apariencia es la más parecida a la de un diamante natural. La ventaja de esta gema es que puede volverse prácticamente incolora, en lugar de tener el tono marrón o amarillo que presentan otros simulantes de diamante. Actualmente, la moissanita sintética se vende como gema por sí misma, sin ser un simulante.
Zirconia cúbica
Esta es la gema de imitación más común y utilizada. Se puede fabricar en una variedad de colores y es un sustituto convincente de algunas gemas. La circonita cúbica no tiene ninguna relación con el circón . Aunque el nombre es similar, son minerales completamente diferentes. Algo así como manzanas y naranjas.
Vaso
Comúnmente utilizado para imitar casi cualquier gema, es la forma más antigua conocida de imitación. Crear vidrio de cualquier color es fácil, por lo que lograr que una gema de vidrio parezca auténtica es fácil con esta imitación.
Plástico
Al igual que el vidrio, el plástico puede utilizarse para imitar muchas piedras preciosas opacas. Puede imitarse con la malaquita o la turquesa, y a veces se utiliza para imitar el ópalo (a menudo llamado opalita).
En las Subastas de Gemas, está prohibida la venta de piedras preciosas sintéticas o de imitación. Puede comprar piedras preciosas totalmente naturales con total confianza.
COMPRE PIEDRAS PRECIOSAS NATURALES
Buscar en el Gemstone Encyclopedia
Subastas relacionadas
Artículos relacionados
Cada persona tiene una piedra preciosa que corresponde a su signo zodiacal. Estas también se conocen como tu Piedra Estelar. Aprende más sobre estas piedras y descubre cuál es tu Piedra Estelar.
10th May 2018
Originalmente, las piedras de nacimiento o gemas se asociaban con un signo zodiacal o el mes de nacimiento de una persona. Descubra cuál es su piedra y vea las que tenemos a la venta.
8th Feb 2021
Hay docenas de gemas de cuarzo y calcedonia con diversos colores y patrones. ¡Aprenda todo sobre las propiedades del cuarzo y cada tipo de cuarzo, desde la amatista y el ágata hasta el cuarzo plasma y el cuarzo fantasma!
15th Oct 2020
últimos artículos
La forsterita es la versión mineral del peridoto de calidad gema, una piedra preciosa semipreciosa de color verde lima a oliva del grupo de especies minerales olivino.
26th Feb 2026
La okenita es un mineral raro, con forma de bola de algodón, conocido por su belleza nubosa. Descubre su significado, valor, consejos de cuidado, historia, orígenes y especificaciones detalladas del mineral en esta guía completa.
17th Feb 2026
Los cristales de heulandita pertenecen a la familia de las zeolitas y tienen forma de ataúd. Suelen ser de color rosa, blanco, verde o naranja, y son potentes cristales curativos. Gem Rock Auctions comparte toda la información sobre los cristales de heulandita.
12th Feb 2026
Categorías de artículos
How To's is where you will find helpful articles from gem Rock Auctions on how to cut gemstones, select gemstones and buy gemstones.
9 Artículos








