
Cosa sono le pietre preziose sintetiche, le imitazioni e i simulanti?
 Nel mondo delle pietre preziose , esistono gemme create per imitare la natura o per cercare di assomigliarle. Queste gemme sono chiamate sintetiche, imitazioni o simulanti. Esploreremo le differenze e quali sono le gemme più comuni sul mercato.
Nel mondo delle pietre preziose , esistono gemme create per imitare la natura o per cercare di assomigliarle. Queste gemme sono chiamate sintetiche, imitazioni o simulanti. Esploreremo le differenze e quali sono le gemme più comuni sul mercato.
Innanzitutto, alcune definizioni
Sintetiche – Le gemme sintetiche sono pietre preziose create dall'uomo ma con una controparte naturale. Possiedono le stesse proprietà fisiche, chimiche e ottiche della pietra naturale.
Imitazione o simulante : si tratta di gemme che cercano di assomigliare a vere gemme naturali, ma sono realizzate con un materiale completamente diverso. Possono essere un'altra gemma (spesso più economica) o un materiale non prezioso come plastica o resina.
Pietre preziose naturali
Le pietre preziose naturali sono qualsiasi minerale estratto dal terreno e tagliato per ottenere una pietra preziosa. Possono essere trattate con diverse tecniche per migliorarne il colore e la purezza, come il riscaldamento, ma il minerale principale deve provenire dalla natura. La creazione di pietre preziose naturali può richiedere milioni di anni e le persone sono rimaste affascinate dalla loro bellezza fin dalla notte dei tempi.

Pietre preziose sintetiche
Le gemme sintetiche sono quelle che imitano esattamente le pietre naturali, ma sono create dall'uomo in laboratorio. Le gemme sintetiche più comuni sono i diamanti sintetici, gli zaffiri sintetici e il quarzo sintetico. Le gemme sintetiche hanno la stessa composizione chimica, struttura cristallina e proprietà delle gemme naturali. È molto difficile per un esperto non qualificato distinguere una gemma sintetica da una naturale.

Gemme imitate o simulate
Le imitazioni o simulanti sono gemme che cercano di assomigliare a quelle vere. Le gemme simulanti o imitazioni più comuni sul mercato sono quelle che cercano di replicare un diamante. Simulanti come il rutilo sintetico o il titanato di stronzio sono stati utilizzati per decenni per cercare di replicare la brillantezza del diamante.
Sebbene queste pietre preziose siano create dall'uomo, non hanno le stesse proprietà fisiche e la stessa composizione chimica delle gemme naturali che imitano. Per questo motivo non sono classificate come sintetiche.
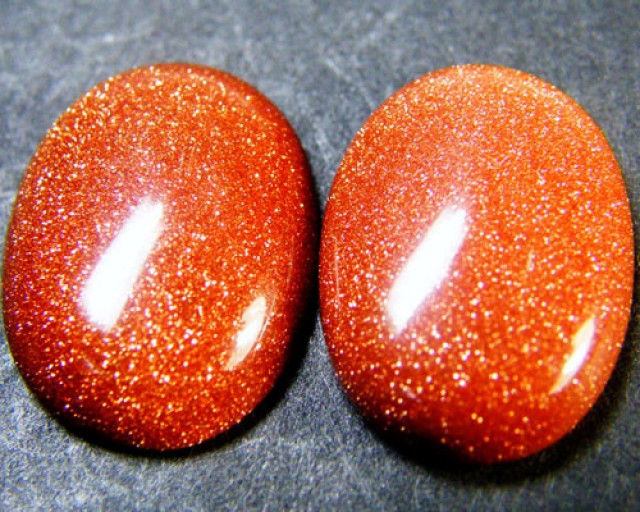
Vetro e plastica sono altre imitazioni comuni. Il vetro blu viene spesso venduto come zaffiro blu ad acquirenti ignari, mentre le perle di plastica possono essere vendute come perle naturali. La goldstone è un vetro artificiale con pagliuzze dorate, spesso venduto come pietra del sole naturale (nella foto sotto).

Quali sono le pietre preziose sintetiche più comuni?
Le pietre preziose sintetiche sono in produzione dai primi anni del 1800, quindi non sono una novità. C'è la convinzione errata che i vecchi gioielli in stile vintage non possano essere sintetici, perché si pensa che la tecnologia utilizzata per creare pietre preziose sintetiche non esistesse a quei tempi. In realtà, i gioielli vintage sono disseminati di pietre preziose sintetiche perché fino a poco tempo fa non esisteva la tecnologia per rilevarle.
La maggior parte dei materiali sintetici è stata originariamente creata per scopi industriali. Il quarzo, in particolare, è utilizzato in molti componenti elettronici. Trovare grandi quantità di quarzo puro e privo di inclusioni è costoso e richiede molto tempo, quindi è stato sviluppato un processo per coltivare il quarzo in laboratorio. In questo modo, il prodotto finale poteva essere controllato. Lo zaffiro sintetico, utilizzato per quadranti di orologi e smartphone, è un altro modo in cui i minerali sintetici vengono creati per l'uso quotidiano.

Con l'introduzione di questa tecnologia è possibile creare materiali di qualità gemma che possono essere sfaccettati. Le gemme sintetiche più comuni sono
Zaffiro o Rubino (il minerale Corindone)
Diamante
Smeraldo
Spinello
Opale
Crisoberillo e Alessandrite
Come vengono create le pietre preziose sintetiche?
Esistono diversi modi per creare gemme sintetiche. Il metodo più antico, noto come fusione a fiamma, è il più semplice ed economico per creare una gemma sintetica. Ogni metodo lascia un'impronta digitale microscopica all'interno della gemma, che può essere utilizzata per la rilevazione.
Fusione a fiamma o processo Verneuil
La polvere contenente gli elementi necessari per creare un minerale viene fatta passare attraverso una fiamma calda, dove si fonde su una piattaforma rotante. Raffreddandosi, il liquido si cristallizza in una pietra preziosa sintetica. Un esempio è l'ossido di alluminio che, riscaldato e raffreddato, si trasforma in corindone (zaffiro o rubino). Spinello , zaffiro e rubino vengono comunemente creati con questo metodo.

Processo Czochralski o metodo di trazione
Questo metodo prevede la fusione di una soluzione ricca di nutrienti in un crogiolo. Per avviare il processo di crescita si utilizza un seme. Un seme è solitamente una piccola quantità del minerale desiderato, ad esempio l'alessandrite . Il seme viene immerso nella soluzione dove inizia la cristallizzazione. Il seme viene lentamente estratto dalla soluzione e, raffreddandosi, la cristallizzazione continua. Le gemme più comuni realizzate con questo metodo sono il crisoberillo e l'alessandrite, il corindone e il granato .

Metodo del flusso
Il metodo Flux è uno dei più costosi per la creazione di gemme sintetiche. Il processo prevede la dissoluzione di un materiale solido, il Flux, con altri nutrienti. Quando la soluzione inizia a raffreddarsi, si formano i cristalli al suo interno. Questo metodo è comunemente utilizzato per gli smeraldi , ma può essere utilizzato anche per spinello, zaffiro, rubino e alessandrite.

Metodo idrotermale
Questo è l'unico metodo noto in grado di creare quarzo sintetico. Se avete familiarità con il modo in cui il quarzo si forma in natura, noterete che viene utilizzato lo stesso termine, ovvero "idrotermale".
Idrotermale significa che si crea in acqua. In natura, quando c'è una cavità nel terreno piena di acqua caldissima e ricca di nutrienti che inizia a raffreddarsi, il quarzo cresce. È così che si formano le geodi di ametista .
Il processo idrotermale imita questo evento naturale creando un ambiente estremamente caldo in cui l'acqua ricca di nutrienti viene lentamente raffreddata. I nutrienti presenti nell'acqua iniziano a cristallizzarsi e a creare quarzo sintetico.
Processo di fusione del cranio
Questo processo viene utilizzato per la creazione di zirconia cubica . È simile al metodo Flux, ma il liquido deve essere surriscaldato. Per contenere il liquido, l'esterno del contenitore viene raffreddato in modo che il liquido si raffreddi e crei una "zucchera" che lo contiene. Raffreddandosi, il liquido crea cristalli perfetti di zirconia cubica.
CVD (deposizione chimica da vapore)
Questo è uno dei due metodi noti per creare diamanti sintetici. I diamanti CVD vengono creati nel vuoto, dove gli atomi di carbonio precipitano lentamente su una base.

HPHT (alta pressione alta temperatura)
I diamanti HPHT vengono creati utilizzando enormi contenitori in acciaio chiamati "presse" per simulare la pressione e la temperatura estreme delle profondità terrestri. Sono in grado di raggiungere oltre 60.000 atmosfere di pressione e temperature fino a 1500 gradi Celsius. Il diamante HPHT più grande attualmente disponibile è una pietra di forma quadrata da 10,02 ct, di colore "E" e purezza VS1.

Quali sono le imitazioni o le pietre preziose più comuni?
Come accennato in precedenza, una pietra preziosa imitata o simulante è qualcosa che cerca di imitare una pietra preziosa naturale, ma è composta da un materiale completamente diverso. Di seguito è riportato un elenco delle imitazioni più comuni.
Spinello sintetico
Lo spinello sintetico è facilmente realizzabile con il metodo Flame Fusion ed è disponibile in una varietà di colori. Lo spinello sintetico è venduto con i nomi di zaffiro, acquamarina o peridoto . È un materiale molto duro, quindi è sensato realizzarne delle imitazioni.
Rutilo sintetico, titanato di stronzio, moissanite sintetica, YAG e GGG
Tutti e cinque questi minerali sono artificiali, sebbene rutilo e moissanite abbiano ciascuno una controparte naturale. Sono stati raggruppati insieme perché il loro uso principale è quello di simulare il diamante. Il rutilo sintetico e il titanato di stronzio (da non confondere con la titanite) hanno entrambi un'incredibile dispersione (il fuoco che si vede nei diamanti), quindi sono comunemente usati in sostituzione dei diamanti. YAG e GGG sono entrambi granati (granato di ittrio e alluminio e granato di gadolinio e gallio) che ricordano l'aspetto dei diamanti.

La moissanite sintetica è il simulante di diamante più recente e il suo aspetto è il più vicino a quello di un diamante naturale. Il bello di questa gemma è che può essere resa quasi incolore, anziché presentare una sfumatura marrone o giallastra tipica di altri simulanti di diamante. Oggigiorno, la moissanite sintetica viene venduta come gemma a sé stante, senza essere venduta come simulante.
Zirconia cubica
Questa è la pietra preziosa d'imitazione più comune e ampiamente utilizzata. Può essere realizzata in una varietà di colori diversi ed è un'ottima alternativa ad alcune pietre preziose. La zirconia cubica non ha nulla a che fare con lo zircone . Sebbene il nome sia simile, si tratta di minerali completamente diversi. Un po' come mele e arance.
Bicchiere
Comunemente utilizzato per imitare quasi tutte le pietre preziose, è la più antica forma di simulante conosciuta. Creare vetro di qualsiasi colore è facile, quindi con questo simulante è facile far sembrare una pietra preziosa di vetro come quella vera.
Plastica
Proprio come il vetro, la plastica può essere utilizzata per imitare molte pietre preziose opache. Può essere realizzata in modo da sembrare malachite o turchese e talvolta viene utilizzata per imitare l'opale (spesso chiamata opalite).
Su Gem Rock Auctions, la vendita di pietre preziose sintetiche o imitazioni è vietata. Puoi acquistare in tutta sicurezza pietre preziose completamente naturali.
ACQUISTA PIETRE PREZIOSE NATURALI
Cerca il Gemstone Encyclopedia
Aste correlate
articoli Correlati
Ognuno di noi ha una pietra preziosa che corrisponde al proprio segno zodiacale. Queste pietre sono anche note come la tua Pietra Stellare. Scopri di più su queste pietre e qual è la tua Pietra Stellare.
10th May 2018
In origine, le pietre portafortuna o gemme erano associate a un segno zodiacale o al mese di nascita di un individuo. Scopri qual è la tua pietra e guarda le pietre che abbiamo in vendita.
8th Feb 2021
Esistono moltissimi strumenti sul mercato per testare una pietra preziosa, ma quali sono i principali strumenti necessari per un'analisi semplice? Diamo un'occhiata a quattro strumenti per testare le pietre preziose.
4th Mar 2020
Articoli Recenti
La forsterite è la versione minerale del peridoto di qualità gemma, una pietra semipreziosa di colore verde lime o verde oliva appartenente al gruppo delle specie minerali dell'olivina.
26th Feb 2026
L'okenite è un raro minerale simile a un batuffolo di cotone, noto per la sua bellezza nebulosa. Scoprine il significato, il valore, i consigli per la cura, la storia, le origini e le specifiche dettagliate in questa guida completa.
17th Feb 2026
I cristalli di heulandite appartengono alla famiglia dei minerali zeolitici e hanno una forma a "bara". Sono comunemente rosa, bianchi, verdi o arancioni e sono potenti cristalli curativi. Gem Rock Auctions condivide tutto ciò che c'è da sapere sui cristalli di heulandite.
12th Feb 2026
Categorie di articoli
How To's is where you will find helpful articles from gem Rock Auctions on how to cut gemstones, select gemstones and buy gemstones.
9 Articoli








