
Zafiro amarillo: propiedades, significados, valor y más
 El zafiro amarillo es un tipo de gema de zafiro que se encuentra en varios tonos de amarillo, incluido el codiciado amarillo canario. El color de estas piedras puede parecerse al de los diamantes amarillos.
El zafiro amarillo es un tipo de gema de zafiro que se encuentra en varios tonos de amarillo, incluido el codiciado amarillo canario. El color de estas piedras puede parecerse al de los diamantes amarillos.
Un apodo común para el zafiro amarillo es “Pukhraj”, que es significativo en varias culturas, mitología y astrología del sur de Asia.
En el ámbito de la joyería, los zafiros amarillos son más asequibles que los zafiros azules o Padparadscha. Este color de zafiro también está en alza, lo que lo convierte en una excelente inversión. Además, su durabilidad lo convierte en una de las mejores piedras para anillos .
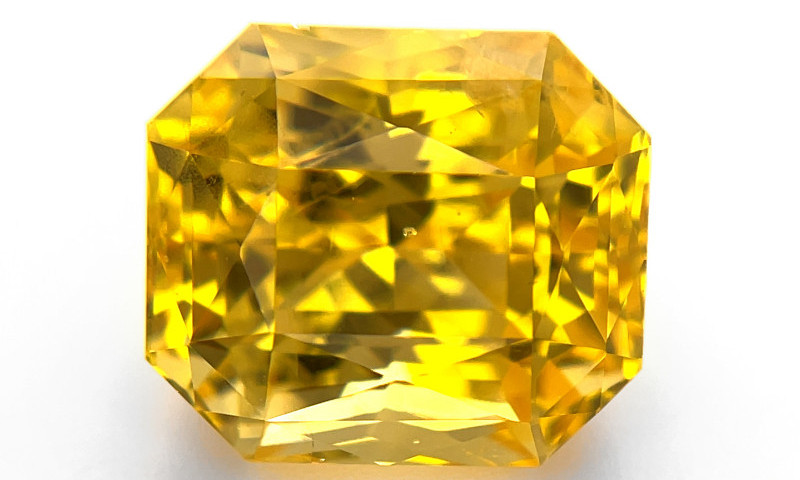

Acerca de la piedra de zafiro amarillo
Los zafiros amarillos son piedras preciosas que pueden parecerse a otras gemas conocidas, como el topacio . Esta semejanza ha dado lugar a nombres comerciales como "Topacio Rey" o "Topacio Oriental", pero estos nombres engañosos infringen las directrices de la FCC.
Otros nombres para el zafiro amarillo incluyen:
Pukhraj (un nombre en hindi que abordaremos más adelante)
Piedra de la sabiduría
Piedra de Júpiter
Todos los zafiros son piedras de nacimiento de septiembre , pero el zafiro amarillo también es piedra de nacimiento de noviembre, junto con el topacio amarillo y el citrino . Los zafiros son gemas tradicionales para el 5.º, 45.º y 75.º aniversario de bodas, así como piedras del zodiaco para el signo Tauro.
Especificaciones y características del zafiro amarillo
El zafiro amarillo es una variedad de corindón , un mineral de óxido de aluminio. Las impurezas de hierro causan su color amarillo. Los zafiros suelen formarse como cristales prismáticos de extremos planos, en forma de barril o bipiramidales.
Se pueden identificar algunos zafiros amarillos con las herramientas gemológicas adecuadas. Con un espectrómetro, se observarán tres líneas de absorción que se fusionan a 4500 en la mayoría de los zafiros. Los zafiros amarillos naturales no presentan líneas de diagnóstico, pero los zafiros amarillos australianos naturales sí presentan líneas a 4500, 4600 y 4700.
Ciertas inclusiones (haces paralelos de diásporo o rutilo) pueden crear zafiros estrella amarillos. Este efecto se denomina asterismo, un fenómeno óptico que crea rayos de luz reflejados con forma de estrella sobre la superficie de la piedra.
Los zafiros amarillos se pueden diferenciar del topacio amarillo o del citrino por su dureza. En la escala de dureza mineral de Mohs , el topacio tiene un valor de 8, mientras que el citrino tiene un valor de 7; ambos son más blandos que el zafiro amarillo.
Hablando de eso, aquí hay una descripción general de las propiedades minerales del zafiro amarillo:
Dureza de Mohs : 9
Color : Tonos de amarillo con posibles matices anaranjados, marrones o verdes; Los especímenes de varios colores pueden ser amarillo y verde o amarillo y azul; Puede haber zonificación de color.
Estructura cristalina : hexagonal (trigonal)
Brillo : Vítreo (vidrioso) a adamantino
Transparencia : Transparente a opaco
Índice de refracción : 1,76-1,77
Densidad : 3,98-4,10
Escote : Ninguno
Fractura : Concoidea
Raya : Blanca
Luminiscencia : Colores de fluorescencia y rayos X presentes; albaricoque distintivo en LW-UV y rayos X, amarillo anaranjado débil en SW-UV (natural); rojo muy débil en SW-UV (sintético)
Pleocroísmo : Presente y muy fuerte en amarillo medio a amarillo pálido.
Birrefringencia : 0,008-0,009
Efectos ópticos : A veces asterismo.
Dispersión : 0,018
Dejando a un lado la mineralogía, ¿qué simboliza un zafiro amarillo?
Significado e historia del zafiro amarillo
Los zafiros amarillos reciben el apodo de "piedra de la sabiduría" y, por lo tanto, simbolizan la sabiduría y la inteligencia espiritual. También representan la prosperidad, la alegría y la conexión celestial, lo que nos lleva a Pukhraj.
 Imagen superior: Anillo con piedra preciosa Navaratna | Crédito de la imagen: Pradeep717, licencia Creative Commons Atribución-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional
Imagen superior: Anillo con piedra preciosa Navaratna | Crédito de la imagen: Pradeep717, licencia Creative Commons Atribución-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional
Zafiro amarillo en hindi: Pukhraj y Navaratna
En la India, el zafiro amarillo se llama "Pukhraj" o "Pukhraj ratna", que significa "joya amarilla", aunque algunas traducciones interpretan "Pukhraj" como una referencia al topacio o al citrino. Términos similares incluyen:
Pushkaraj
Empujar Raja
Peetmani
Kanakapushyaragam
En cualquier caso, Pukhraj está vinculado al planeta Júpiter en la astrología védica (hindú). Júpiter es el planeta más beneficioso en la astrología hindú, y se dice que quienes llevan Pukhraj atraen sus beneficios para la riqueza, la buena suerte y el éxito.
También apodado “piedra de Júpiter”, el zafiro amarillo es una de las nueve gemas planetarias que componen el Navaratna.
Navaratna significa "nueve gemas" en sánscrito y describe un estilo de joyería cultural que contiene nueve piedras preciosas, cada una representando un cuerpo planetario de nuestro sistema solar. Esta joyería no solo es común en el hinduismo, sino también en el budismo, el sijismo y el jainismo.
El significado o poder de las joyas de Navaratna varía desde simbolizar el estatus hasta representar a los Navagrahas , o “nueve dioses celestiales”, de la astrología hindú.
El color y la calidad del zafiro también son importantes. El zafiro azul representa a Saturno o "Shani". Algunas culturas asiáticas creen que solo las gemas perfectas son beneficiosas en el Navaratna, mientras que las gemas defectuosas son perjudiciales.
Además, el mejor dedo para llevar un anillo de zafiro amarillo (según los astrólogos hindúes) es el dedo índice derecho porque este dedo, llamado Tarjani en sánscrito, está regido por Júpiter.

Historia
La palabra «zafiro» tiene dos posibles raíces etimológicas. Una es el griego antiguo sappheiros , que significa «piedra azul», relacionado con «zafiro», que describía al lapislázuli y otras gemas azules hasta la Edad Media.
Otro posible origen es el sánscrito śanipriya , que significa “sagrado para Saturno”, relacionado con la asociación del zafiro azul con Saturno en la astrología hindú.
Como muchos zafiros, los primeros zafiros amarillos conocidos provienen de Sri Lanka. La minería de zafiro en Sri Lanka se remonta a más de 2000 años.
Desde la década de 1960, Australia se ha convertido en una importante fuente de zafiros. Si bien la mayoría son azules, los zafiros amarillos australianos presentan una coloración notablemente brillante. Unos pocos son bicolores (o particolores) en amarillo y verde o amarillo y azul.
Las amarillas y verdes a veces se llaman zafiros "acacia". La acacia (o mimosa) es la flor nacional de Australia. Tiene flores de color amarillo dorado y hojas de color verde oliva.
Volviendo a lo metafísico, ¿cuál es el poder del zafiro amarillo?

Propiedades curativas del zafiro amarillo
El zafiro amarillo, como cualquier gema, puede ser una piedra curativa . Este cristal, junto con otras gemas amarillas, ofrece mayor esperanza, éxito y alegría.
Además, las piedras preciosas amarillas son excelentes piedras para el chakra del plexo solar, equilibrando el centro energético para que te sientas seguro y en control.
¿Cuáles son los beneficios del zafiro amarillo a nivel físico y emocional?
Curación física
Los beneficios comúnmente atribuidos al zafiro amarillo para el bienestar físico incluyen el tratamiento o mejora de:
Desintoxicación
Función del sistema linfático
Insomnio
Concentración
Sanación emocional
Los zafiros amarillos pueden aportar equilibrio emocional y autoconciencia. Se cree que esta piedra fomenta el ingenio y las metas ambiciosas.
Además, se dice que el zafiro amarillo reduce la ansiedad, aumenta la satisfacción en las relaciones y fortalece la toma de decisiones.

Propiedades de la piedra preciosa de zafiro amarillo
El valor del zafiro amarillo depende de su color, corte, claridad, peso en quilates, tratamientos y origen (natural o sintético).
Color
El mejor tono de zafiro amarillo es un amarillo canario brillante de tono medio, apreciado tanto como gema como para fines astrológicos. Los tonos amarillo limón también son valiosos.
Las impurezas de hierro suelen causar el color amarillo, y un mayor contenido de hierro implica una mayor saturación. Sin embargo, la radiación (ya sea natural o inducida por laboratorio) también puede crear tonos soleados.
Ampliando este tema, los expertos del Instituto Gemológico de América (GIA) han estudiado la estabilidad del zafiro amarillo a la luz (tendencia a desteñirse con la exposición prolongada a la luz solar).
Encontraron 7 tipos de zafiro amarillo relacionados con el origen del material (natural vs. sintético), el agente que causa el color y la estabilidad:
Tipo 1: Natural; Centro de color; Estable a la luz
Tipo 2: Natural o tratado con irradiación; Centro de color; Se desvanece
Tipo 3: Natural; Contiene hierro y sin calentar; Estable a la luz.
Tipo 4: Natural; Contiene hierro y se calienta; Estable a la luz.
Tipo 5: Natural o sintético; tratado por difusión; estable a la luz
Tipo 6: Sintético; Sin tratamiento; Estable a la luz
Tipo 7: Sintético; Tratado con irradiación; Se decolora
Curiosamente, los zafiros amarillos tipo I pueden desteñirse al calentarse, pero la exposición a la luz recuperará su color.
Cortar
Muchos zafiros amarillos están facetados y prácticamente cualquier forma es posible. Los mejores cortes (proporcionales, simétricos, sin zonas oscuras) alcanzan los precios más altos.
Los zafiros estrella amarillos deben tallarse como cabujones para que su "estrella" luzca bien. Los ejemplares de menor calidad también pueden tallarse como cabujones.
Claridad
Los zafiros tienen un grado de claridad de piedra preciosa de color Tipo II, lo que significa que se esperan algunas inclusiones pequeñas y visibles.
Las inclusiones comunes incluyen:
Bandas de color hexagonales o líneas de crecimiento
Huellas dactilares
Cristales de circón , a menudo con fracturas oscuras en forma de “halo”
Varios cristales (por ejemplo, granate , hematita , corindón, espinela)
En comparación con los zafiros azules o rosas , los zafiros amarillos generalmente tienen menos inclusiones.

Peso en quilates
Los cristales de zafiro amarillo pueden ser bastante grandes, lo que da lugar a gemas de alto quilataje. Las gemas de más de 2 quilates generalmente solo aumentan ligeramente su precio por quilate.
Algunos de los zafiros amarillos más grandes incluyen:
La Piedra del Centenario : zafiro amarillo australiano de 2.020 quilates hallado en 1979, robado en 1980, pero recuperado en 1986
Zafiro “Willows” : zafiro amarillo australiano de 217,5 quilates hallado en 1946 en los campos de gemas Willows de Queensland.
The Autumn Glory : zafiro australiano de color amarillo a naranja de 103,5 quilates encontrado en 1993, pero desaparecido desde que fue enviado a EE. UU.
El Tomahawk Tiger : zafiro amarillo australiano de 82,4 quilates con bandas de color distintivas
Otro zafiro amarillo notable está en el anillo que la actriz de Bollywood Madhuri Dixit Nene ha usado desde que se convirtió en actriz, similar a muchas estrellas de Bollywood.
Tratos
Los zafiros amarillos naturales de alta calidad son bastante escasos, por lo que los joyeros pueden compensar la diferencia mediante tratamientos o piedras sintéticas. Los tratamientos de calor e irradiación son comunes para mejorar la coloración, pero las gemas irradiadas pueden desteñirse por la exposición a la luz solar. La difusión es otro tratamiento menos común.
A veces, los zafiros de Sri Lanka de color blanco lechoso, llamados “geudas”, se calientan para volverse azules, amarillos o naranjas.
Sintéticos: Cómo identificar el zafiro amarillo original
El zafiro amarillo sintético se crea en un laboratorio, pero tiene la misma composición química y física que el material natural. Estos zafiros son más impecables que los naturales y constituyen una opción más económica y sostenible.
Menos deseables son los simuladores : diferentes gemas u otros materiales utilizados para imitar zafiros amarillos.
¿Cómo puedo saber si mi zafiro amarillo es auténtico ? Algunos indicadores de un zafiro falso (simulador) o creado en laboratorio son:
Burbujas de gas (simulante)
Arañazos (quizás simulados)
Estrías curvas, líneas de crecimiento y/o bandas de color (sintéticas)
Inclusiones de huellas dactilares (quizás sintéticas)
Velos ahumados (sintéticos)
Inclusiones de “cabeza de clavo” (sintéticas)
Volviendo a la realidad, ¿cómo se forma el zafiro amarillo natural?
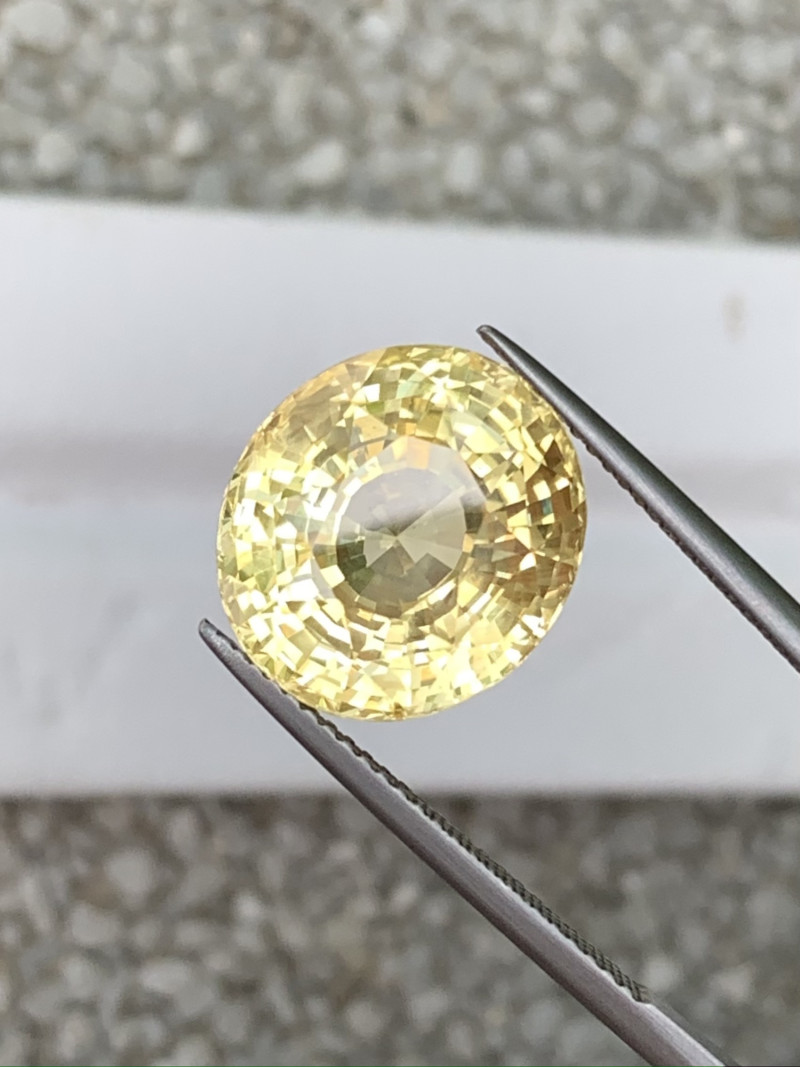
Formación y fuentes del zafiro amarillo
Las piedras de corindón como el zafiro amarillo se forman dentro de rocas metamórficas o ígneas.
En las rocas ígneas, la piedra cristaliza al enfriarse a partir del magma. Un enfriamiento más prolongado crea cristales más grandes. La roca ígnea debe ser rica en aluminio y pobre en sílice, como las sienitas nefelínicas .
En las rocas metamórficas, los cristales a menudo se forman cuando los antiguos fondos marinos sufren metamorfismo a partir de aguas calientes ricas en aluminio.
Muchas veces, las rocas que contienen los zafiros se desgastan, lo que permite que el agua arrastre las gemas hacia depósitos aluviales, como los lechos de los ríos.
Ubicaciones mineras
Los zafiros amarillos de alta calidad provienen de Sri Lanka y Myanmar. Se dice que son el segundo tipo de zafiro más abundante en Sri Lanka.
Otras fuentes notables de zafiro amarillo son:
Australia
Porcelana
Madagascar
Tanzania
Tailandia
¡Una vez cortados y vendidos, salen al mercado!

Precio y valor del zafiro amarillo
En primer lugar, ¿son caros los zafiros amarillos? Comparados con los zafiros azules o Padparadscha , los zafiros amarillos son mucho más asequibles, pero su precio varía considerablemente.
Los precios de las piedras de zafiro amarillo facetadas varían entre $50 y $750 por quilate de menos de 2 quilates y entre $375 y $1,625 por quilate de más de 2 quilates.
Los raros zafiros amarillos australianos bicolores (facetados) tienen un precio de venta al por mayor de entre $100 y $1,050 por quilate. Otras gemas sueltas de zafiro amarillo australiano se venden entre $100 y $400 por quilate, y algunas superan los $1,500 por quilate.
Los zafiros estrella amarillos se venden por entre 100 y 300 dólares por quilate cuando son de 0,5 a 1 quilate, y por entre 100 y 500 dólares por quilate cuando son de 1 a 5 quilates.
Cuidado y mantenimiento del zafiro amarillo
Por último, hablaremos del cuidado de las piedras preciosas . Primero, ¿cuánto dura el zafiro amarillo? Depende.
Las piedras naturales sin tratar deberían durar toda la vida con un mantenimiento adecuado. Las piedras con muchas inclusiones o fracturas serán más frágiles. Algunas joyas son más vulnerables que otras; por ejemplo, un collar de zafiro amarillo será menos vulnerable que un anillo.
Aun así, los zafiros amarillentos mediante irradiación natural o inducida en laboratorio se decoloran con la exposición prolongada a la luz solar. Esto es delicado, ya que dejar un zafiro amarillo a la luz solar intensifica su color, pero la exposición prolongada provoca la decoloración.
Lamentablemente, se sabe que muchos zafiros amarillos y Padparadscha pierden color, pero depende del “tipo” descrito en la sección Color.
La forma más segura de limpiar esta piedra es con un cepillo de dientes suave, agua tibia y jabón suave.
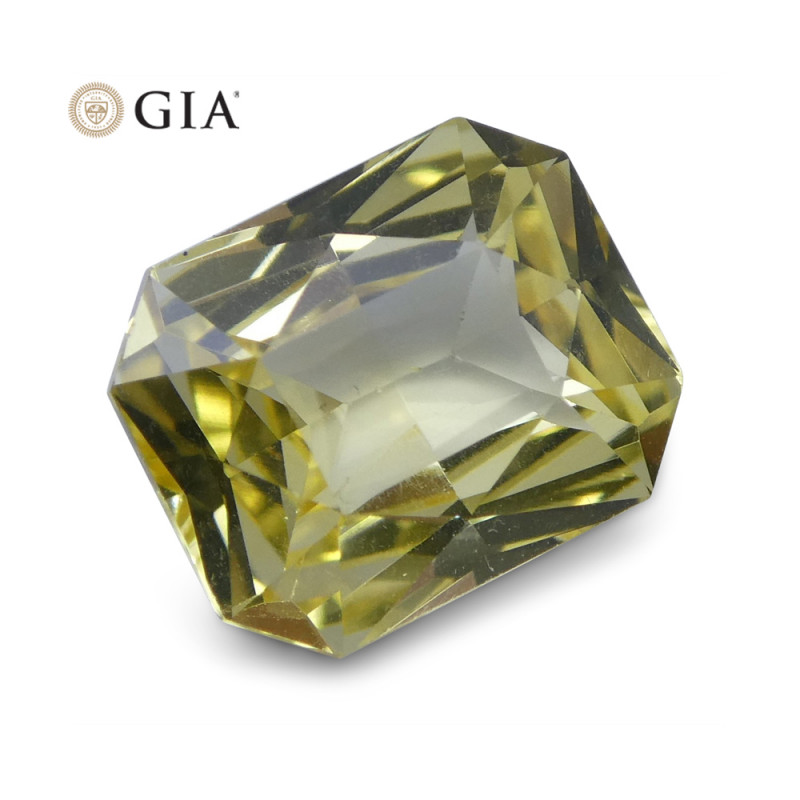

¡Levántate y brilla en Yellow Sapphire!
Con opciones que van desde tonos limón pastel hasta dorados vibrantes, hay zafiros amarillos para todos los gustos. Ya sea que uses un zafiro amarillo como anillo Pukhraj, en una joya Navaratna o simplemente como accesorio de moda, ¡definitivamente brillarás como el sol!
Buscar en el Gemstone Encyclopedia
Subastas relacionadas
Artículos relacionados
Cada persona tiene una piedra preciosa que corresponde a su signo zodiacal. Estas también se conocen como tu Piedra Estelar. Aprende más sobre estas piedras y descubre cuál es tu Piedra Estelar.
10th May 2018
Originalmente, las piedras de nacimiento o gemas se asociaban con un signo zodiacal o el mes de nacimiento de una persona. Descubra cuál es su piedra y vea las que tenemos a la venta.
8th Feb 2021
Hay docenas de gemas de cuarzo y calcedonia con diversos colores y patrones. ¡Aprenda todo sobre las propiedades del cuarzo y cada tipo de cuarzo, desde la amatista y el ágata hasta el cuarzo plasma y el cuarzo fantasma!
15th Oct 2020
últimos artículos
Las tallas de marfil de palma, también llamadas marfil vegetal, son una alternativa natural al marfil de elefante, extraído éticamente de la nuez de palma de la palmera sudamericana Phytelephas. ¡Aprenda todo sobre el marfil de palma en esta guía!
15th Jan 2026
Las piedras de flores de crisantemo son maravillas naturales que presentan un patrón floral de calcita blanca, celestita o andalucita sobre piedra caliza negra o lutita.
13th Jan 2026
La piedra solar reticulada arcoíris es una variedad de feldespato con tres magníficos efectos ópticos causados por la presencia de diversas inclusiones. Su vibrante colorido y su patrón reticular la convierten en una rara joya de colección.
12th Jan 2026
Categorías de artículos
How To's is where you will find helpful articles from gem Rock Auctions on how to cut gemstones, select gemstones and buy gemstones.
9 Artículos



![MASSIVE BRECIATED MOOKAITE 298 GRAMS [[MX928 ]](https://liveplatforms-production.b-cdn.net/tenants/gr/uploads/images/75000-79999/75508/75508_1233708971.jpg?width=480&aspect_ratio=1001%3A1000)

![MASSIVE FLUORITE GOLD -BRILLIANT COLOURS 135 CTS [S2199]](https://liveplatforms-production.b-cdn.net/tenants/gr/uploads/images/50000-54999/51509/51509_1222410585.jpg?width=480&aspect_ratio=1001%3A1000)
